Private Health Insurance
Ian McCarthy | Emory University
Table of contents
- History of Health Insurance
- Employer Sponsored Insurance
- Non-group Coverage
Background
Early history of health insurance
- 1929: “Hospital insurance” for schoolteachers to receive care from Baylor University Hospital in Dallas, TX
- Essentially pre-paid medical care for about 1,500 schoolteachers in the area
- Annual fee (or “premium”) of $6 per year, $104 in 2023, for up to 21 days of hospital care
- Subscription model offered regular cash flow for hospitals
Early history of health insurance
- Popular revenue model for hospitals
- Network of hospitals grew to be Blue Cross, first established in Sacramento, CA in 1932
- Structure introduces a few distortions:
- Care concentrated in hospitals, even if other settings could provide care at lower cost
- No price competition
- Care concentrated in hospitals, even if other settings could provide care at lower cost
- Blue Cross plans grew in the 1930s
- Operated as a not-for-profit
- Exempt from typical regulations on insurance markets
- Operated as a not-for-profit
Early history of health insurance
- Expansion into prepaid physician services (Blue Shield), combined to be Blue Cross and Blue Shield
- By 1940, half of all health insurance plans were Blue Cross and Blue Shield plans
- Hospitals paid on a cost-plus basis (more on this later)
- Any competing insurance plans had to offer the same structure
What if?
Imagine Congress had created a national program in the 1930s instead of leaving insurance to Blue Cross/Blue Shield.
- How might U.S. health insurance look different today?
- Would employers play the same role?
Modern health insurance
Where do you think most non-elderly Americans get their insurance today?
- Employers
- Direct purchase
- Medicaid
- Uninsured
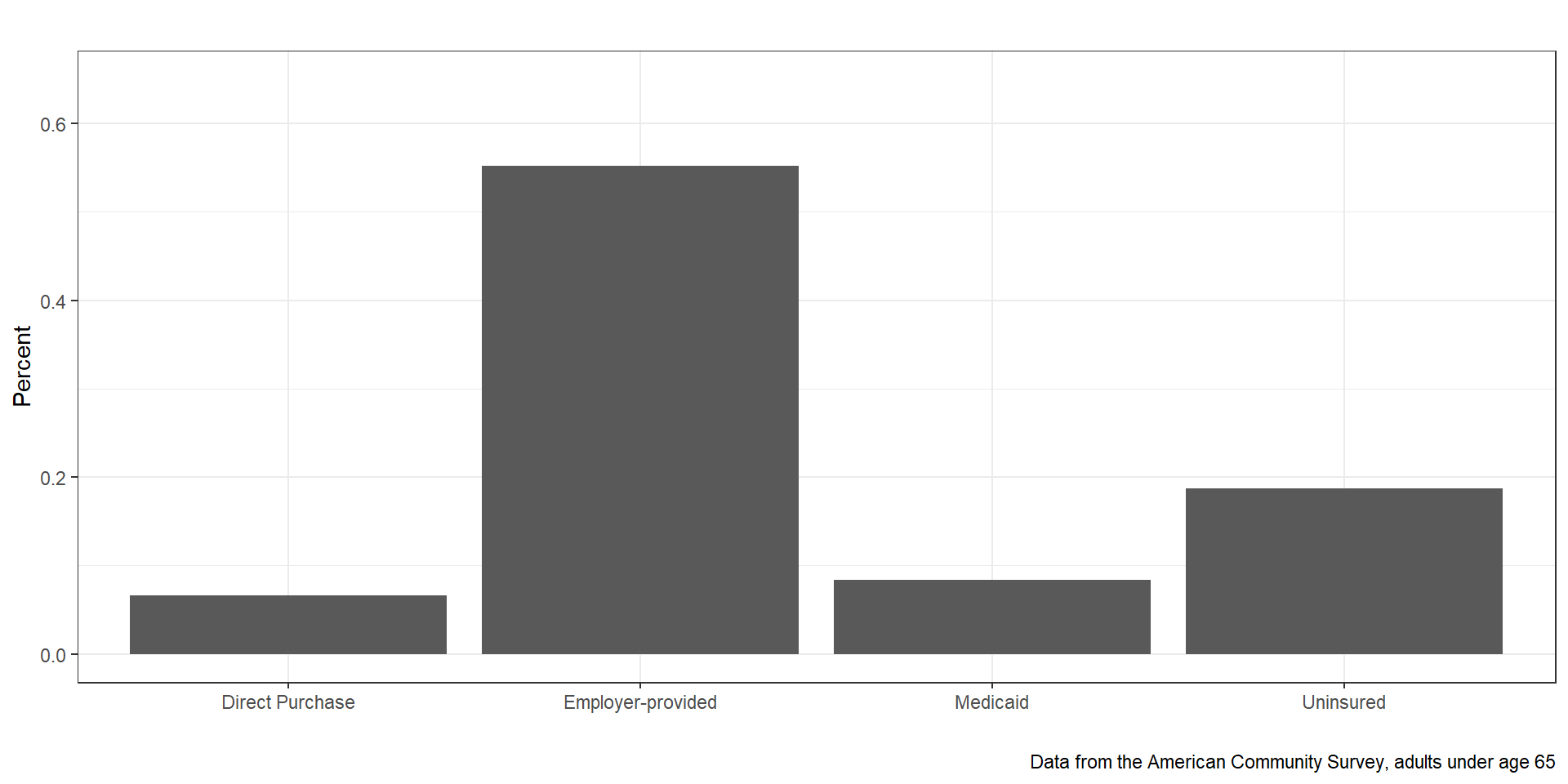
Figure 1: Source of Health Insurance (2012)
Employer-sponsored Insurance
Why dependent on ESI?
- Stabilization act of 1942 (wages frozen but not benefits)
- Tax exemption for insurance expenditures (1954)
How does ESI work?
- Employer pays large share of premium
- Employee pays smaller share “pre-tax”
- Often only a few plan options
- Many large employers are “self-funded”
- Employer actually pays for the health care
- Insurer is an administrator and negotiator
- Avoids state mandated benefits and state premium taxes (ERISA laws)
- Useful for employers across state lines
- Employer actually pays for the health care
Non-group coverage
What is “non-group” coverage?
- Health insurance plans purchased by individuals directly from insurers, rather than being obtained through employers or government programs
- Possibly more choices, depending on where you live
- Premiums vary based on factors such as age, location, and (historically) pre-existing conditions
- Significant changes with the implementation of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) in the United States, which introduced marketplaces where individuals can compare and purchase health insurance plans, along with subsidies to help lower-income individuals afford coverage
Big changes in non-group options from the ACA
- Health insurance marketplaces
- Essential health benefits
- Pre-existing condition protections
- Subsidies and financial assistance
- Coverage requirements and individual mandate
- Mandate challenged in Supreme Court and upheld at first
- Effectively removed in 2019 when penalty was set to $0
- Mandate challenged in Supreme Court and upheld at first
Imagine yourself
You are 28, self-employed, and living in Georgia
- What insurance options do you have before the ACA?
- What changed in 2014?